
Why Aero’s Surefill Heat Stress Response Kits Belong on Every Jobsite
Working in high temperatures can be dangerous—especially for outdoor crews and industrial workers. That’s why every jobsite should be equipped with Aero Heat Stress Response Kits. Designed for fast response and hydration, these kits help prevent serious heat-related illness before it escalates.
When heat stress strikes, time is critical. That’s why having a Heat Stress Response Kit on hand can make all the difference.
Aero Healthcare’s Surefill Kits: Your First Line of Defense
At Southern Safety Supply, we recommend Aero Healthcare’s Surefill Heat Stress Response Kits because they’re specifically designed for rapid, effective response in hot environments.
Whether you’re running a construction crew, managing a road work project, or preparing for outdoor summer events, these kits help you stay compliant, prepared, and safe.
What’s Inside the Surefill Heat Stress Kits?
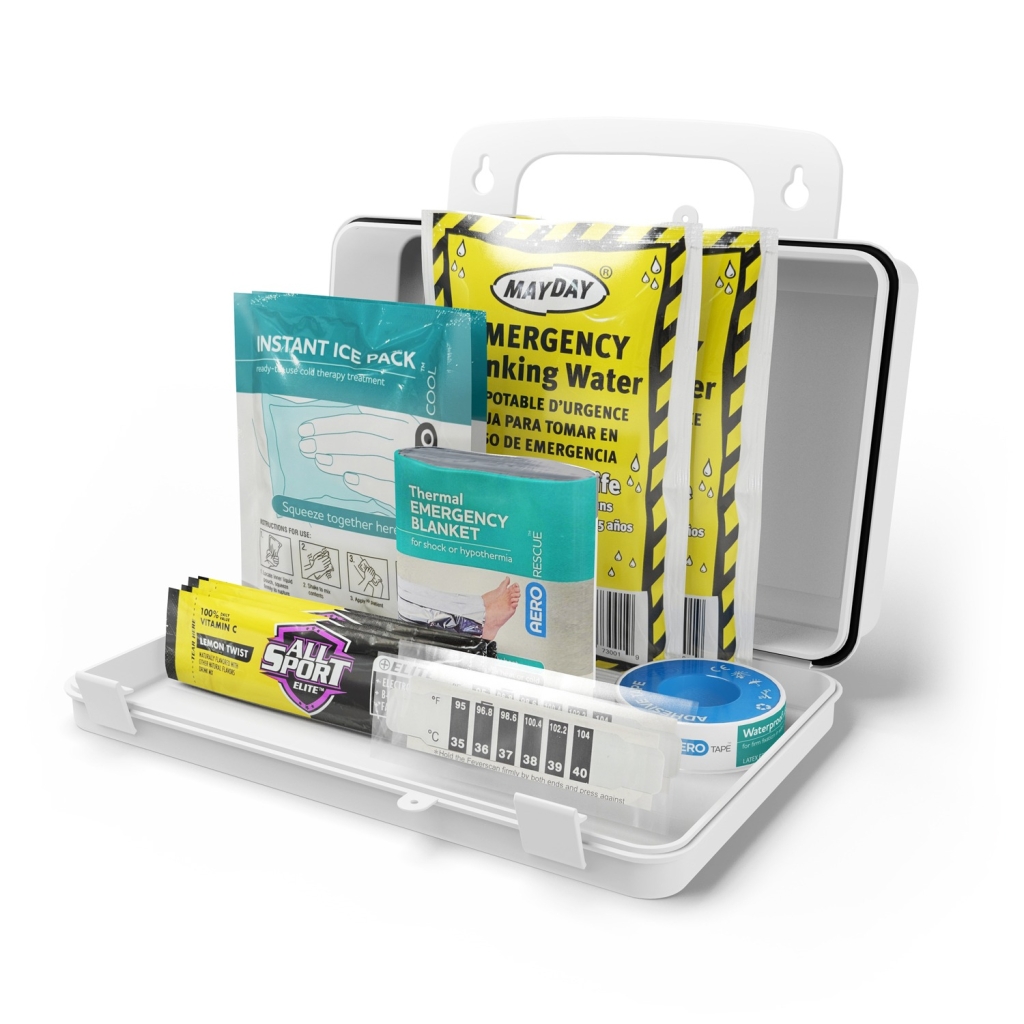

Each kit is packed with essential cooling and hydration supplies to help manage heat-related emergencies right on the spot:
- Cold packs for rapid temperature reduction
- Thermal blankets to help stabilize body heat
- Electrolyte drink powder to replenish fluids fast
- Drinking water pouches for immediate hydration
- Electrolyte tablets (available in large kits)
With compact and portable packaging, these kits are built for quick deployment anywhere—job sites, warehouses, delivery fleets, or outdoor work zones.
Who Needs These Kits?
If your team works outdoors or in high-heat indoor conditions, heat stress kits should be a standard part of your workplace safety gear.
Industries that benefit from Surefill Heat Stress Kits include:
- Construction
- Transportation & delivery
- Manufacturing
- Agriculture
- Event staffing
- First responders
Stay Compliant. Stay Ready.
According to OSHA, employers must provide a safe work environment—including protection from heat-related hazards. Aero’s Heat Stress Kits support compliance with heat illness prevention protocols and demonstrate your commitment to employee well-being.
Don’t Wait—Call to Order Before the Heat Peaks
As summer temperatures rise, so does the demand for heat stress supplies. Aero’s Surefill Heat Stress Response Kits are in high demand during peak heat months, and availability can be limited. Ensure your crew is protected before the next heatwave hits.
📞 Call us today to place your order and get your kits delivered in time for the season. Whether you’re gearing up for a busy construction schedule or prepping outdoor teams, now is the time to act.
Stay Ahead of Summer Hazards
Be sure to follow us on Facebook for ongoing National Safety Month tips, workplace safety gear updates, and seasonal promos. Sign up for our Monthly Safety Newsletter to stay informed and prepared.
Let’s keep safety simple—and summer heat survivable.
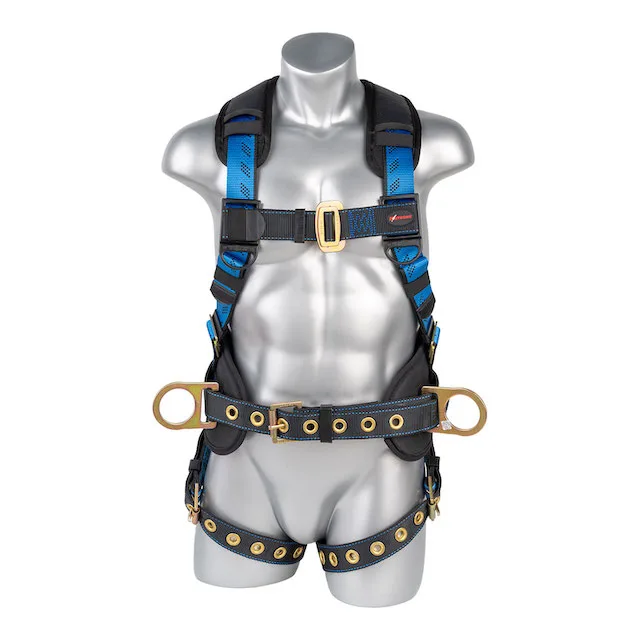


















 What Makes a Good Body Support Harness?
What Makes a Good Body Support Harness?